[vc_row type="in_container" full_screen_row_position="middle" scene_position="center" text_color="dark" text_align="left" overlay_strength="0.3" shape_divider_position="bottom" bg_image_animation="none"][vc_column column_padding="no-extra-padding" column_padding_position="all" background_color_opacity="1" background_hover_color_opacity="1" column_link_target="_self" column_shadow="none" column_border_radius="none" width="1/1" tablet_width_inherit="default" tablet_text_alignment="default" phone_text_alignment="default" column_border_width="none" column_border_style="solid" bg_image_animation="none"][vc_column_text]
 IEEE has launched the International Network Generations Roadmap (INGR) on the topic "Connecting the Unconnected (CTU) with 5G and B5G". Sudhir Dixit and Ashutosh Dutta, the Co-chairs of the working group, have invited 12 co-authors for contribution to the roadmap document.
IEEE has launched the International Network Generations Roadmap (INGR) on the topic "Connecting the Unconnected (CTU) with 5G and B5G". Sudhir Dixit and Ashutosh Dutta, the Co-chairs of the working group, have invited 12 co-authors for contribution to the roadmap document.
The document contains a detailed analysis of the main challenges for connecting the unconnected, being:
- Low population density
- Sparse and clustered settlements
- Comparatively lower income levels
- Remote and difficult to access regions
- Inadequate grid-based power supply
- Price-benefit comparison with urban/suburban areas
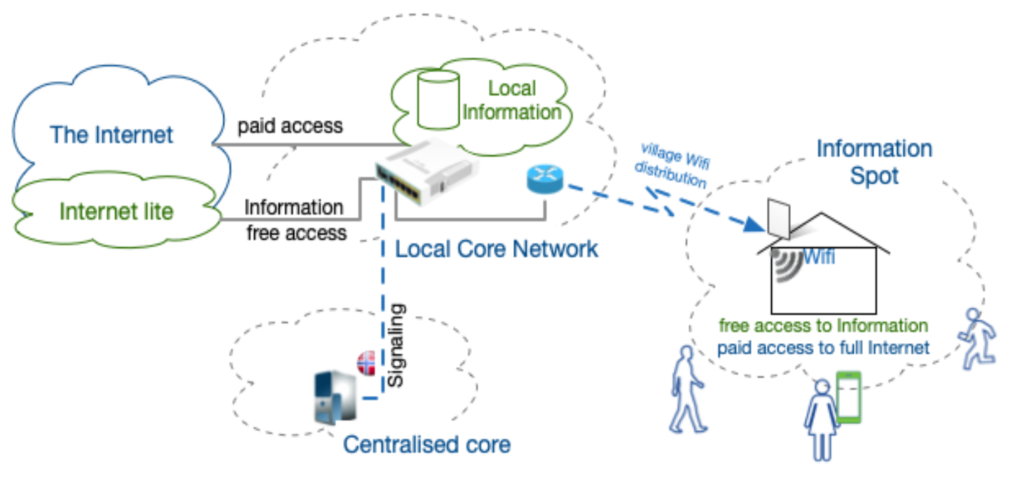
Amongst solutions being discussed are the use of TV White Space, Community networks and the Freemium Model suggested by the Basic Internet Foundation (see Figure 2, as described in the roadmap document).
We are pleased to see that our work is recognised,
- first by the United Nations High-Level Panel on Digital Cooperation,
- then by the Government of Norway in the White Paper to the Parliament,
- by the 6G Flagship project on 6G and the SDGs and
- now by IEEE as a roadmap for "Connect the Unconnected".
Be invited to go through the attached abstract, or download the full Roadmap "Connect the Unconnected" from IEEE directly.
Abstract of the IEEE International Network Generations Roadmap (INGR) on "Connecting the Unconnected (CTU) with 5G and B5G"
Connecting the Unconnected or under-connected (CTU) is the holy grail of transforming the lives of over 3 billion people around the globe with wireless Internet who are yet to experience its value in multiple ways. If this could be accomplished, its impact on the society would be enormous. This white paper from the IEEE Future Networks CTU Working Group endeavors to highlight the need to consider the CTU requirements in 5G and B5G networks in the standardization process, in the development of the use cases, and affordable solutions.
In its Vision 2030 SDG (Sustainability Development Goals) the United Nations has proclaimed access to Internet as basic human right and has said that these goals cannot be achieved without affordable access to Internet by everyone on this planet. While there are numerous projects and initiatives ongoing around the world, but these are fragmented and lack the critical mass and coordination to be able to impact the future standards, product development, and cost of deployment otherwise achievable by volume.
The CTU WG and this white paper intends to create a single platform where the experts can bring their ideas, solutions, and potentially collaborate to create large global projects and influence the network service providers, manufacturers and their governments. This white paper defines the CTU working group’s charter, scope, and provides a brief overview of the relevant stakeholders and linkages between them. Then the paper goes into the current status of the CTU landscape and where we want to reach to accomplish the vision of connecting everybody, especially those living in rural and remote areas. We present the various standards and industry fora and how they are interlinked. While technologies are available today, they need to be customized and optimized at the systems level to bring down the cost of network in order to be affordable. In addition, the content needs to be relevant and in local languages to be of useful, not to mention the need to offer innovative HCI solutions (that are not text based) so that people who are not literate or digitally disadvantaged can easily use the devices and consume services.
Another important area is that of flexible spectrum allocation regime at the lower range of the spectrum to increase reach and coverage. Use of renewable energy sources will enable deployment in remote areas where there is lack of power grid or it is intermittent. Thus, this white paper identifies a number of technology gaps to be filled in 5G and B5G networks, such that access is affordable and content and services are actually consumed by the target set of users. Technology aside, need to develop innovative business models is a must to be commercially sustainable in the long-term. A number of such models, especially designed for the rural population, are proposed, such as Village Level Entrepreneur (VLE) Freemium (Free + Premium), revenue sharing among the chain of service providers, subsidized billing by USOF (Universal Service Obligation Funds). Finally, the white paper presents a 10-year roadmap starting from the current state to 3 years, 5 years and 10 years.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]

Recent Comments